Carbon-confined ultrasmall T-Nb2O5 nanocrystals anchored on carbon nanotubes by pyrolysing MLD-niobiumcone films for enhanced electrochemical applications†
Abstract
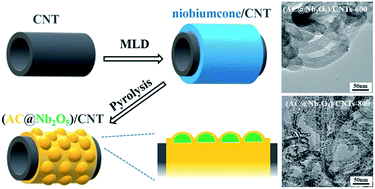
Nb2O5 electrode materials encounter a great challenge for electrochemical applications due to their poor electrical conductivity and undesirable thermal sintering. The emerging molecular layer deposition (MLD) technique provides a feasible route to solve the problems in the synthesis and application of materials. In this work, conformal ultrathin niobiumcone films with a high carbon content are synthesized on carbon nanotubes (CNTs) by MLD using niobium ethoxide and hydroquinone. Nb2O5 nanocrystals and amorphous carbon (AC) are produced during the subsequent pyrolysis of niobiumcone films under nitrogen. More importantly, Nb2O5 nanocrystals are both confined in the carbon shell and anchored on the surface of carbon nanotubes to form an (AC@Nb2O5)/CNTs composite. This structure contributes to suppress the undesirable sintering of Nb2O5 for achieving a small nanocrystal size and uniform particle dispersion. Therefore, the (AC@Nb2O5)/CNTs composite shows great potential as an anode material in lithium/sodium-ion batteries and supercapacitors. As an electrochemical application evaluation, orthorhombic (AC@Nb2O5)/CNTs-800 with a nanocrystal size of ∼6 nm exhibits high specific capacity, excellent cycling stability and superior rate capability. The enhanced electrochemical performance is attributed to the synergistic effect of material characteristics including the optimization of the crystal phase for efficient lithium ion intercalation, the downsizing of nanocrystals for a short ions/electron transport path, the introduction of carbon materials for high electrical conductivity, and the encapsulation/anchoring of nanocrystals for high interfacial/structural stability. This work provides a significant insight into the reasonable design of advanced electrode materials for high-performance lithium/sodium-ion storage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...