Effect of lithium incorporation on tweaking the electrocatalytic behavior of tantalum-based oxides†
Abstract
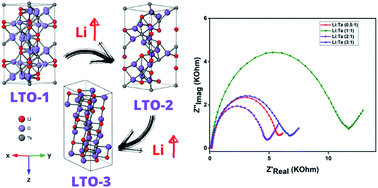
To study the effect of lithium incorporation on the electrochemical properties and catalytic behavior of tantalum-based oxides, a series of mesoporous lithium-contained tantalum oxides was developed adopting an inverse micelle-based sol gel synthesis method. Four various phases of amorphous Ta2O5, polycrystalline LiTaO3, Li5.04Ta6.16O17.92, and Li3TaO4 were determined for samples synthesized at Li/Ta ratios of 0.5 (LTO-0.5), 1 (LTO-1), 2 (LTO-2), and 3 (LTO-3) respectively. The surface analysis revealed that LTO-2 sample is featured with lower amount of lithium atoms at the surface rather than the bulk of the sample. The electrochemical analysis of LTO samples showed that LTO-2 possesses lower charge transfer resistance extracted from impedance spectroscopy that consequently leads to a better electrocatalytic performance. The LTO-2 electrode also showed a low open circuit potential (OCP) combined with a relatively higher electroactive surface area, thus capable of running an electrooxidation reaction at a potential lower than all other LTO samples. The more negative OCP value of LTO-2 electrode in AA solution states a more facile electron transfer between the analyte and electrode compared to other synthesized samples. Mott–Schottky plots of LTO electrodes are characterized by positive slopes which indicate n-type semiconductor behavior. The charge carrier density (5.5 × 1019 cm−3) in LTO-2 sample is the lowest among all other samples. The charge carrier density is dependent on the amount of applied lithium in the synthesis confirming various lithium diffusion behaviors in LTO samples. The lower carrier concentration in LTO-2 justifies its higher activity in electrooxidation providing less populated lower unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) for the accommodation of electrons extracted from the analyte higher occupied molecular orbital (HOMO). Therefore, LTO-2 showed an improved electrocatalytic performance due to lower charge transfer resistance (higher conductivity) offered by lower amount of lithium atom at its surface and higher oxygen vacancies in the bulk.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...