Safety issues of defective lithium-ion batteries: identification and risk evaluation†
Abstract
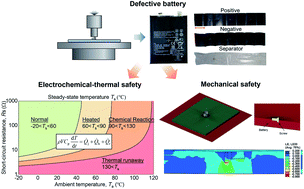
Lithium-ion batteries inevitably suffer minor damage or defects caused by external mechanical abusive loading, e.g., penetration, deformation, and scratch without triggering a hard/major short circuit. The replacement of cells becomes a dilemma if the safety risk of the defective batteries remains unknown. Herein, by introducing a representative defect form, i.e., screw indentation, we demonstrate the safety characteristics of defective batteries. We prove that defective batteries have a significantly increased thermal risk and deteriorated mechanical integrity, but can go undetected due to prompt voltage recovery and insignificant local temperature increase. We discover that the voltage curve within the first few cycles contains sufficient information to identify defective batteries from otherwise good ones and propose methodologies to monitor the cells. Capacity loss and current leakage are two characteristics that can be estimated using the voltage curve. According to the defect size and position, the capacity loss could be 1 to 102 mA h and the leakage current could be 5–50 mA. Results remove the barriers for defective battery safety risk evaluation, enabling identification, monitoring, and early warning of minor damaged batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...