Operando structural and chemical evolutions of TiS2 in Na-ion batteries†
Abstract
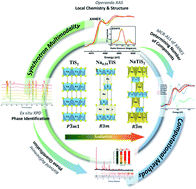
Titanium disulfide (TiS2) with high electric conductivity, fast rate capability, and good cycling performance is a promising candidate for electrode material in sodium (Na)-ion batteries. Despite the well-studied electrochemical behaviors of TiS2 in Li-ion batteries, the detailed reaction mechanism of TiS2 in Na-ion batteries is not yet fully understood due to a more complex multi-phase conversion process. In this work, reactions of TiS2 in Na-ion batteries are investigated via a multi-modal synchrotron approach: operando X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy (XAS) – including X-ray Absorption Near-Edge Structure (XANES) and Extended X-ray Absorption Fine Structure (EXAFS) – and ex situ X-ray Powder Diffraction (XPD), coupled with computational modeling. Operando XANES spectra indicate that the redox reactions occur in both Ti and S during the electrochemically driven phase transformation. Multivariate Curve Resolution-Alternating Least Squares (MCR-ALS) analysis of XAS suggests that different numbers of components are involved in the lithiation and sodiation of TiS2, with the sodiation including at least one intermediate phase in addition to the starting material and the final sodiation product. Ex situ XPD and Rietveld refinement further determined and quantified the unknown phases, showing that three phases, TiS2, Na0.55TiS2, and NaTiS2, participate in the sodiation of TiS2. Operando EXAFS results show the changes in the Ti–Ti coordination number and interatomic distance. This explains the coulombic efficiency decay due to the incomplete recovery of the coordination number of Ti after cycling. Overall, this work reveals the reaction mechanism occurring in Na–TiS2 batteries with a greater quantitative understanding of the structural evolution. By combining the multi-modal synchrotron approach and computational work, this study provides a framework for studying a broader range of electrochemically driven phase-transformation systems towards advanced energy storage and conversion applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...