Chiral stresses in nematic cell monolayers
Abstract
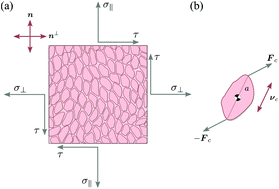
Recent experiments on monolayers of spindle-like cells plated on adhesive stripe-shaped domains have provided a convincing demonstration that certain types of collective phenomena in epithelia are well described by active nematic hydrodynamics. While recovering some of the hallmark predictions of this framework, however, these experiments have also revealed a number of unexpected features that could be ascribed to the existence of chirality over length scales larger than the typical size of a cell. In this article we elaborate on the microscopic origin of chiral stresses in nematic cell monolayers and investigate how chirality affects the motion of topological defects, as well as the collective motion in stripe-shaped domains. We find that chirality introduces a characteristic asymmetry in the collective cellular flow, from which the ratio between chiral and non-chiral active stresses can be inferred by particle-image-velocimetry measurements. Furthermore, we find that chirality changes the nature of the spontaneous flow transition under confinement and that, for specific anchoring conditions, the latter has the structure of an imperfect pitchfork bifurcation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...