Disruption of microtubule function in cultured human cells by a cytotoxic ruthenium(ii) polypyridyl complex†
Abstract
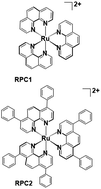
Treatment of malignant and non-malignant cultured human cell lines with a cytotoxic IC50 dose of ∼2 μM tris(4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)ruthenium(II) chloride (RPC2) retards or arrests microtubule motion as tracked by visualizing fluorescently-tagged microtubule plus end-tracking proteins. Immunofluorescent microscopic images of the microtubules in fixed cells show substantial changes to cellular microtubule network and to overall cell morphology upon treatment with RPC2. Flow cytometry with MCF7 and H358 cells reveals only minor elevations of the number of cells in G2/M phase, suggesting that the observed cytotoxicity is not tied to mitotic arrest. In vitro studies with purified tubulin reveal that RPC2 acts to promote tubulin polymerization and when imaged by electron microscopy, these microtubules look normal in appearance. Isothermal titration calorimetry measurements show an associative binding constant of 4.8 × 106 M−1 for RPC2 to preformed microtubules and support a 1 : 1 RPC2 to tubulin dimer stoichiometry. Competition experiments show RPC2 does not compete for the taxane binding site. Consistent with this tight binding, over 80% of the ruthenium in treated cells is co-localized with the cytoskeletal proteins. These data support RPC2 acting as an in vivo microtubule stabilizing agent and sharing many similarities with cells treated with paclitaxel.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...