Detection of key transient Cu intermediates in SSZ-13 during NH3-SCR deNOx by modulation excitation IR spectroscopy†
Abstract
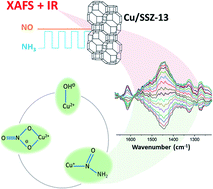
The small pore zeolite Cu-SSZ-13 is an efficient material for the standard selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides (NOx) by ammonia (NH3). In this work, Cu-SSZ-13 has been studied at 250 °C under high conversion using a modulation excitation approach and analysed with phase sensitive detection (PSD). While the complementary X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy measurements showed that the experiments were performed under cyclic Cu+/Cu2+ redox, Diffuse Reflectance Infrared Fourier Transform Spectroscopy (DRIFTS) experiments provide spectroscopic evidence for previously postulated intermediates Cu–N(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O)–NH2 and Cu–NO3 in the NH3-SCR deNOx mechanism and for the role of [Cu2+(OH−)]+. These results therefore help in building towards a more comprehensive understanding of the reaction mechanism which to date has only been postulated in silico.
O)–NH2 and Cu–NO3 in the NH3-SCR deNOx mechanism and for the role of [Cu2+(OH−)]+. These results therefore help in building towards a more comprehensive understanding of the reaction mechanism which to date has only been postulated in silico.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...