Design, synthesis and bioevaluation of novel 6-substituted aminoindazole derivatives as anticancer agents†
Abstract
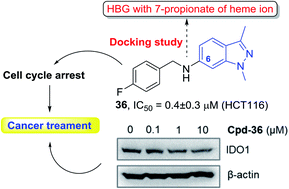
In the present study, a series of 6-substituted aminoindazole derivatives were designed, synthesized, and evaluated for bio-activities. The compounds were initially designed as indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) inhibitors based on the structural feature of five IDO1 inhibitors, which are currently on clinical trials, and the important anticancer activity of the indazole scaffold. One of them, compound N-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-indazol-6-amine (36), exhibited a potent anti-proliferative activity with an IC50 value of 0.4 ± 0.3 μM in human colorectal cancer cells (HCT116). This compound also remarkably suppressed the IDO1 protein expression. In the cell-cycle studies, the suppressive activity of compound 36 in HCT116 cells was related to the G2/M cell cycle arrest. Altogether, the current findings demonstrate that compound 36 would be promising for further development as a potential anticancer agent.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...