Surface refined AuQuercetin nanoconjugate stimulates dermal cell migration: possible implication in wound healing†
Abstract
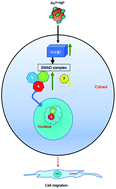
Refining nutraceutical conjugated metal nanoparticles (NPs) and understanding their interactions with the cellular micro-environment is necessary for their application in nanomedicine. In the present experiment, we studied the effect of quercetin functionalized gold nanoparticles (AuQurNP) on skin fibroblast and keratinocyte cell migration. Spherical shaped AuQurNPs of 47 nm in size were formed due to the interaction of hydroxyl and carbonyl groups of quercetin with Au atoms as revealed by incremental algorithm-based analysis. AuQurNP containing up to 5 μg l−1 of Au with quercetin (5.2 ± 1.6 ng ml−1) was least toxic to fibroblasts. AuQurNP effectively reduced the generation of intracellular ROS (up to 63%) through free-radical scavenging activity. AuQurNP also enhanced the rate of migration of fibroblasts (24 h) and keratinocytes (20 h) in artificially created wounds. The rate of migration of the cells towards the wound edge was in the order of AuQurNP > control > quercetin > AuNP. AuQurNP also significantly increased the expression of TGFβ1 protein, thereby inducing the downstream SMAD complex (SMAD 2–4). Downregulation of the inhibitory protein SMAD 7 by AuQurNP helped in the nuclear translocation of SMADs 3 and 4. Collectively, the present in vitro study demonstrates the action of AuQurNP on the SMAD family and the interconnected molecular mechanism leading to the cell migration process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...