Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking study of novel pyridoxine–triazoles as anti-Alzheimer's agents†
Abstract
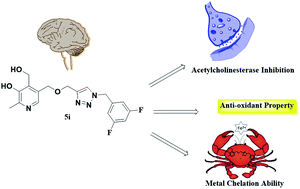
A series of multi-target natural product-pyridoxine based derivatives were designed, synthesized, characterized and evaluated as anti-Alzheimer agents. In vitro testing revealed the multi-functional properties of compounds such as inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), antioxidant and metal chelation. Among the series, 5i derivative was found most potent AChE inhibitor, possess antioxidant potential and chelating metal ions. Further binding interaction of 5i with AChE was studied using molecular docking, showed interaction with both PAS and CAS site of AChE. In silico predictions were also performed to predict toxicity and ADME properties of the molecule 5i and found within drug likeness range. Therefore, 5i could be a promising multi-functional compound that can be used for further development of novel drug for Alzheimer disease.
- This article is part of the themed collection: A Decade of Progress in Click Reactions Based on CuAAC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...