Enhanced thermal stability, hydrophobicity, UV radiation resistance, and antibacterial properties of wool fabric treated with p-aminobenzenesulphonic acid†
Abstract
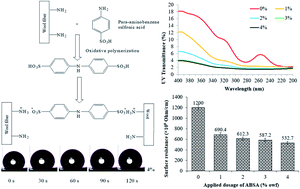
Wool fibre is a popular fibre for the manufacture of apparel and floor coverings, but it does not have adequate thermal stability, antistatic, UV resistance, and antibacterial properties that are required for some applications, such as outerwear and hospital gowns. In this work, a wool fabric was treated with para-aminobenzenesulphonic acid (ABSA) by the oxidative polymerisation method and its effect on the thermal stability, UV radiation resistance, electrical conductivity and antibacterial properties of the treated fabric was systematically evaluated. It was found that the ABSA treatment had synergistic effects on the various functional properties of the treated fabric. The ABSA treatment not only made the fabric antibacterial but also enhanced its UV radiation absorption capability, surface hydrophobicity, electro-conductivity, tensile strength, and thermal stability. The maximum degradation temperature of the wool fibre increased from 339.5 °C to 349.6 °C and the UV-B transmission through the fabric at 290 nm reduced to 1.5%. The surface hydrophobicity of the treated fabric samples also improved as the surface contact angle of the fabric increased from 119.5° for the untreated to 131.7° for the fabric treated with 4% ABSA. The surface electrical resistance decreased from 1200 × 109 to 484 × 109 Ohm cm−1, and the treated fabric also showed excellent antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae. The developed treatment could be used in the textile industry as an energy-efficient process for the multi-functionalisation of wool and other polyamide fibres.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...