Stable antibacterial polysaccharide-based hydrogels as tissue adhesives for wound healing†
Abstract
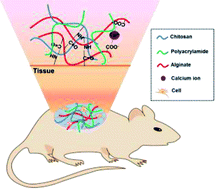
Adhesion to the surface of moist, dynamic, biological tissues is important in many fields. Currently, tissue adhesives commonly used in clinical practice remain far from ideal, exhibiting either poor tissue compatibility or weak tissue adhesion. Here, we designed biocompatible hydrogels comprising polysaccharides with polyacrylamide and exhibiting promising cytocompatibility, antibacterial activity, and excellent tissue adhesion. Alginate/chitosan-based hydrogels covalently cross-linked to the tissue surface in order to achieve admirable tissue adhesion. Additionally, the mechanical properties of the hydrogels were significantly enhanced with the addition of polyacrylamide, which synergistically promoted their enhanced adhesion. Importantly, the hydrogels exhibited good biocompatibility and reasonable antibacterial activity that promoted wound recovery during use as wound dressings. These results suggested the efficacy of the developed tissue adhesives for applications in biomedical fields, as well as broadening potential hydrogel use in tissue engineering.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...