Continuous flow synthesis of phase transition-resistant titania microparticles with tunable morphologies†
Abstract
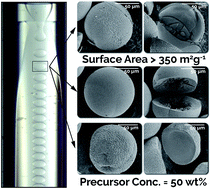
Titania microspheres have attracted substantial attention for a variety of applications, including ion scavenging, catalysis, and energy generation, though most synthetic techniques are limited to a few basic morphologies and narrow size ranges. Here, an intensified microfluidic strategy for continuous synthesis of anatase titania microspheres is presented. In-flow photo crosslinking, incorporated with a flow reactor and polar aprotic solvent, enables access to precursor compositions up to an order of magnitude higher than those previously reported, with size tunability approaching two orders of magnitude. Morphological and surface area effects associated with precursor composition are explored, resulting in hollow, yolk–shell, macroporous, and dense titania microspheres containing no detectable rutile phase and possessing surface areas exceeding 350 m2 g−1 post calcination. Furthermore, effects of calcination temperature and time on the surface area, crystallinity and phase composition, and morphology of the synthesized titania microspheres are studied in detail. The synthesized microspheres are shown to remain completely in the anatase phase, even at temperatures up to 900 °C, far beyond the expected phase transition temperature. Thus, the breadth of attainable morphologies, specific surface areas, and phase compositions present a variety of intriguing substrate candidates for such applications as heterogeneous (photo) catalysis, adsorption and ion capture, electrochemistry, and photovoltaics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...