Excitation dependent visible and NIR photoluminescence properties of Er3+, Yb3+ co-doped NaBi(MoO4)2 nanomaterials†
Abstract
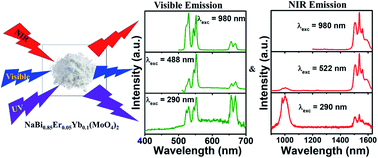
Due to the exceptional luminescence properties of lanthanide doped nanomaterials, they have applications in various field such as sensing, photocatalysis, solar cells, bio-imaging, therapy, diagnostics, anti-counterfeiting, latent fingerprint development, optical amplifiers, solid state lighting, etc. Here, we report the excitation dependent photoluminescence properties of Yb3+, Er3+ co-doped NaBi(MoO4)2 nanomaterials in both the visible and NIR regions upon UV, visible and NIR excitation. These photoluminescence properties show that strong energy transfer occurs from the host to the Yb3+, Er3+ ions. These materials show major emission bands at 530, 552 (green) and 656 nm (red) in the visible region and 1000 and 1534 nm in the NIR region. The intensity ratio between green and red bands is dependent on the excitation wavelength, whereas the intensity ratio of the 1000 and 1534 nm bands relies on the excitation wavelength and Er3+ doping concentration. These materials also exhibit host emission and upconversion luminescence properties in the visible region.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...