Colloidal quantum dot light-emitting diodes employing solution-processable tin dioxide nanoparticles in an electron transport layer
Abstract
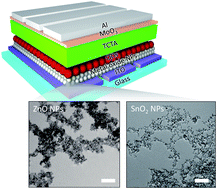
Colloidal quantum-dot-based light-emitting diodes (QD-LEDs) have gained tremendous attention as great candidates to potentially replace current emissive display technologies. The luminescence efficiency of a QD LED has increased rapidly in the past decade; this was triggered by the use of metal oxides in the charge transport layers, particularly zinc oxide (ZnO) for the electron transport layer (ETL). However, the ZnO ETL often results in undesirable device performance such as efficiency roll-off and poor device stability because of excessive electron injection into the QD emissive layer. Here, we explore solution-processable tin dioxide (SnO2) nanoparticles (NPs) as alternatives to ZnO NPs for the ETL in QD-LEDs. We evaluated the thin-film quality and electrical performance of SnO2 NPs and then applied them to the ETL for constructing QD-LEDs. As a result of the smooth surface morphology, moderate electron-transport ability, and lower carrier concentration compared to ZnO NPs, the QD-LED with SnO2 NP-ETL exhibited improved performance in terms of lower turn-on and operating voltages, maximum luminance, improved efficiency roll-off, and improved power efficiency over the reference device with the ZnO NP-ETL. This shows promising potential for SnO2 NPs in optoelectronic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...