Effective estimation of the inhibitor affinity of HIV-1 protease via a modified LIE approach†
Abstract
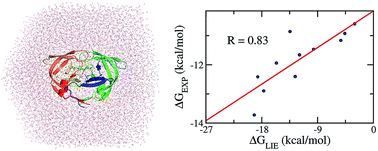
The inhibition of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Protease (HIV-1 PR) can prevent the synthesis of new viruses. Computer-aided drug design (CADD) would enhance the discovery of new therapies, through which the estimation of ligand-binding affinity is critical to predict the most efficient inhibitor. A time-consuming binding free energy method would reduce the usefulness of CADD. The modified linear interaction energy (LIE) approach emerges as an appropriate protocol that performs this task. In particular, the polar interaction free energy, which is obtained via numerically resolving the linear Poisson–Boltzmann equation, plays as an important role in driving the binding mechanism of the HIV-1 PR + inhibitor complex. The electrostatic interaction energy contributes to the attraction between two molecules, but the vdW interaction acts as a repulsive factor between the ligand and the HIV-1 PR. Moreover, the ligands were found to adopt a very strong hydrophobic interaction with the HIV-1 PR. Furthermore, the results obtained corroborate the high accuracy and precision of computational studies with a large correlation coefficient value R = 0.83 and a small RMSE δRMSE = 1.25 kcal mol−1. This method is less time-consuming than the other end-point methods, such as the molecular mechanics Poisson–Boltzmann surface area (MM/PBSA) and free energy perturbation (FEP) approaches. Overall, the modified LIE approach would provide ligand-binding affinity with HIV-1 PR accurately, precisely, and rapidly, resulting in a more efficient design of new inhibitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...