Asymmetric molecular modification of viologens for highly stable electrochromic devices†
Abstract
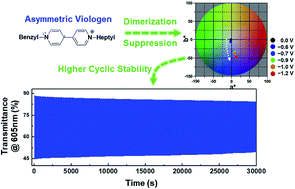
Viologens are one of the most well-known electrochromic (EC) chromophores. In particular, symmetric dialkyl viologens have been widely used in EC devices (ECDs), but suffer from the formation of viologen radical cation dimers that deteriorate device performance. In this work, we propose an effective route to suppress dimer formation through molecularly altering one of the N-substituents. We prepare 1-benzyl-1′-heptyl viologens and find that such asymmetric molecular structures attribute to the suppression of dimer production when used as EC chromophores. The suppression of dimer formation allows us to drive the device at relatively higher voltages, so that we could achieve viologen-based ECDs showing large transmittance changes between colored and bleached states, efficient and fast coloration, and stable coloration/bleaching cyclic operation. The results indicate that high-performance ECDs can be realized by utilizing viologens containing asymmetric molecular structures.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...