3D printed composites from heat extruded polycaprolactone/sodium alginate filaments and their heavy metal adsorption properties†
Abstract
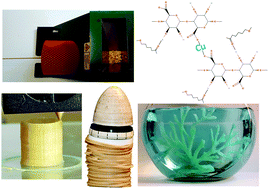
Removal of heavy metals can be achieved through the adsorption of metal ions onto the surfaces of various materials and composites that either have such properties naturally or are modified to obtain those capabilities. Sodium alginate (SA), a marine polysaccharide, is well known for its heavy metal adsorption ability. In this work, we combined polycaprolactone (PCL), a bio-based thermoplastic polymer, with SA with the use of a solvent and the resulting films were inserted into a heat extruder to create PCL/SA filaments. Such PCL/SA filaments were preferred compared to films, since they have greater stability in water and can be used in additive manufacturing technology. Hydrogen bonds are supposed to be formed between the hydroxyl groups of SA and the carbonyl groups of PCL. The resulting composite filaments with SA were able to adsorb heavy metals such as copper ions in water, which was used as a model, with maximum adsorption capacity around 90 mg g−1. Such innovative filaments were used with 3D printing technology to additively manufacture composite structures able to remediate environments contaminated with heavy metals. The filaments were tested with a commercial 3D pen, a 3D printer capable of fused deposition modelling and a plant-inspired self-growing robot. The resulting printed structures were able to adsorb copper ions as the free-standing filaments did.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Open Access Articles in Frontiers Journals


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...