Lithium and magnesium polymeric electrolytes prepared using poly(glycidyl ether)-based polymers with short grafted chains†
Abstract
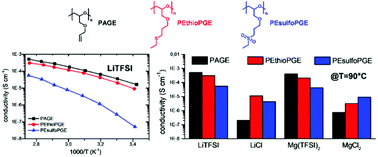
Recently, poly(allyl glycidyl ether) (PAGE) has attracted great interest as a polymer electrolyte for Li-ion transport with conductivity values well above that of the benchmark polyethylene oxide polymer at temperatures below 60 °C. Here, we prepared lithium and magnesium polyelectrolytes by using two novel PAGE-based matrixes containing thioether and sulfone functionalities located in a short side chain inserted by the chemical post-functionalization of PAGE. The synthesized PAGEs, poly(2-(ethyl thio) propyl glycidyl ether) (PEthioPGE) and poly(2-(ethyl sulfone) propyl glycidyl ether) (PEsulfoPGE), were all amorphous at any temperature with Tg between −80 °C and −30 °C. These polymers were used to formulate electrolytes with different Li and Mg salts. The impact of the side chain, used salt and temperature on the ionic conductivity was studied in detail. Ionic conductivities as high as 5.1 × 10−4 S cm−1 at 90 °C can be achieved using PAGE–LiTFSI and PEthioPGE–LiTFSI, values comparable to that achieved using PEO–LiTFSI with identical salt loading. When LiCl is used, PEthioPGE outperforms all other polymers including PEO with the highest conductivity value at 90 °C (1.1 × 10−5 S cm−1). Moreover, the studied complexes with magnesium salts showed promising ionic conductivities, comparable to those achieved using lithium and up to 4.1 × 10−4 S cm−1 at 90 °C for PAGE–Mg(TFSI)2. The results presented here highlight the possibility of tuning the structures and the complexation properties of poly(glycidyl ether)-based electrolytes towards both lithium and magnesium ions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...