Introducing electrical conductivity to metal–organic framework thin films by templated polymerization of methyl propiolate†
Abstract
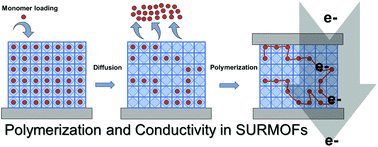
We herein present a case study on the templated, Pd-catalyzed polymerization reaction of methyl propiolate in the confined pore space of three different surface anchored metal–organic framework (SURMOF) systems in order to introduce electrical conductivity to MOF thin films and provide predictions for potential device integrations. To gain comprehensive insight into the influence of the template on polymerization, we chose Cu(bpdc), Cu2(bdc)2(dabco) and HKUST-1 because of their different types of pore channels, 1D, quasi-1D and 3D, and their free pore volumes. Well-defined MOF thin films were prepared using layer-by-layer deposition, which allows for the application of several characterization techniques not applicable for conventional powder MOFs. With SEM, AFM, XRD, MALDI-ToF/MS, ToF-SIMS and QCM, we were able to investigate the behaviour of the polymer formation. For lower dimensional pore channels, we find a depot-like release of monomeric units leading to top-layer formation determined by desorption kinetics, whereas for the 3D channels, quick release of an excess amount of monomers was observed and polymerization proceeds perfectly. Despite polymerization issues, control over the maximum chain lengths and the molecular weight distribution was achieved depending on the dimensionality of the pore systems. For the HKUST-1 system, polymerization was optimized and we were able to measure the electrical conductivity introduced by the conjugated polymer inside the channels.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Editor’s Choice: Functional MOFs and COFs

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...