Heritable nanosilver resistance in priority pathogen: a unique genetic adaptation and comparison with ionic silver and antibiotics†
Abstract
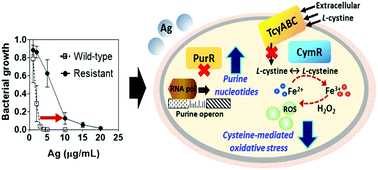
The past decade has seen the incorporation of antimicrobial nanosilver (NAg) into medical devices, and, increasingly, in everyday ‘antibacterial’ products. With the continued rise of antibiotic resistant bacteria, there are concerns that these priority pathogens will also develop resistance to the extensively commercialized nanoparticle antimicrobials. Herein, this work reports the emergence of stable resistance traits to NAg in the WHO-listed priority pathogen Staphylococcus aureus, which has previously been suggested to have no, or very low, capacity for silver resistance. With no native presence of genetically encoded silver defence mechanisms, the work showed that the bacterium is dependent on mutation of physiologically essential genes, including those involved in nucleotide synthesis and oxidative stress defence. While some mutations were uniquely associated with resistance to NAg, the study also found common mutations that could be protective against both NAg and ionic silver. This is consistent with the observation of NAg/ionic silver cross-resistance. These mutations were detected following withdrawal of the silver exposure, denoting heritable characteristics that allow for spread of the resistance traits even with discontinued silver use. Heritable silver resistance in priority pathogen cautions that these nanoparticle antimicrobials should only be used as needed, to preserve their efficacy for treating infections.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...