Pivotal role of N and Bi doping in CQD/Mn3O4 composite structure with outstanding visible photoactivity
Abstract
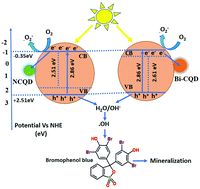
Herein, the effect of N and Bi-doped carbon quantum dots (CQDs) on enhancing the photocatalytic activity of Mn3O4 was compared. The formation of tetragonal Mn3O4 nanoparticles was confirmed by XRD. SEM depicted a densely packed irregular-shaped nanoparticle matrix while HRTEM revealed fringes corresponding to the characteristic planes of the various elements present in the composites. The functional groups representing the elements present in the synthesized nanomaterials were analysed via FTIR. XPS confirmed the N and Bi doping in the synthesized CQDs composites. The UV-Vis DRS analysis showed a reduction in the bandgap energies of the composite photocatalysts. The addition of N- and Bi-doped CQDs resulted in a reduction in PL intensity. The photocatalytic performance of the developed nanocomposites was compared in the solar-driven degradation of bromophenol blue. The photocatalytic efficiency of Mn3O4 was greatly improved in the composites with the highest effect shown by 2.0 mL-NCQDs/Mn3O4. The remarkably boosted photocatalytic efficiency is ascribed to the excellent charge separation and charge transfer ability of the doped carbon quantum dots.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...