Biomedical nanomaterials for immunological applications: ongoing research and clinical trials
Abstract
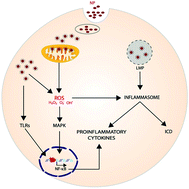
Research efforts on nanomaterial-based therapies for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and cancer have spiked and have made rapid progress over the past years. Nanomedicine has been shown to contribute significantly to overcome current therapeutic limitations, exhibiting advantages compared to conventional therapeutics, such as sustained drug release, delayed drug degradation and site-specific drug delivery. Multiple nanodrugs have reached the clinic, but translation is often hampered by either low targeting efficiency or undesired side effects. Nanomaterials, and especially inorganic nanoparticles, have gained criticism due to their potential toxic effects, including immunological alterations. However, many strategies have been attempted to improve the therapeutic efficacy of nanoparticles and exploit their unique properties for the treatment of inflammation and associated diseases. In this review, we elaborate on the immunomodulatory effects of nanomaterials, with a strong focus on the underlying mechanisms that lead to these specific immune responses. Nanomaterials to be discussed include inorganic nanoparticles such as gold, silica and silver, as well as organic nanomaterials such as polymer-, dendrimer-, liposomal- and protein-based nanoparticles. Furthermore, various approaches for tuning nanomaterials in order to enhance their efficacy and attenuate their immune stimulation or suppression, with respect to the therapeutic application, are described. Additionally, we illustrate how the acquired insights have been used to design immunotherapeutic strategies for a variety of diseases. The potential of nanomedicine-based therapeutic strategies in immunotherapy is further illustrated by an up to date overview of current clinical trials. Finally, recent efforts into enhancing immunogenic cell death through the use of nanoparticles are discussed.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Nanomaterials applied to life sciences, Editor’s Choice: Recent breakthroughs in nanobiotechnology and Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...