Self-stratification of amphiphilic Janus particles at coating surfaces†
Abstract
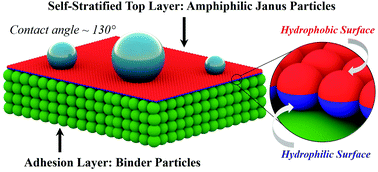
Amphiphilic Janus particles are mixed with homogeneous binder particles with strong adhesion to create robust hydrophobic coatings through a unique self-stratification process. Intriguingly, Janus particles form a complete and densely packed monolayer with their hydrophobic sides orienting towards air, which effectively increases the water contact angle to ∼130°, while the hydrophilic sides sustain strong adhesion with the coating layer. The coating maintains its high contact angle even after solvent rinsing, whereas conventional coating completely breaks down. Experimental data and preliminary theoretical modeling suggest that the stratification are partially due to the strong adsorption of Janus particles at the water–air interface, although the detailed mechanisms require more thorough investigation. Remarkably, simply adding Janus particles renders a hydrophilic commercial primer coating surface hydrophobic and drastically reduces the surface tackiness. This cost-effective and commercially scalable method offers a convenient way to fabricate advanced structures at the interface and can be broadly applicable to many other colloidal systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...