Integrative platform for the selective recovery of intracellular carotenoids and lipids from Rhodotorula glutinis CCT-2186 yeast using mixtures of bio-based solvents†
Abstract
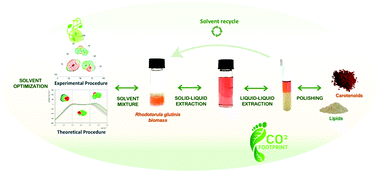
Natural bioactive compounds have been attracting growing interest from the industries as a “greener” alternative to synthetic raw materials/products. Rhodotorula glutinis yeast naturally synthesizes added value compounds such as lipids and carotenoids, commonly used for cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and food applications. R. glutinis constitutes a rigid cell-wall structure, requiring energy-saving and efficient cell disruption methods for a sustainable recovery of the intracellular compounds. A simple and ecofriendly technology using mixed bio-based solvents (biosolvents) was evaluated here as an alternative platform to permeabilize yeast cells and to improve the selective recovery of β-carotene, torularhodin, torulene and lipids. The extraction ability of pure and solvent mixtures (methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate, isopropanol, cyclohexane and 2-methyl tetrahydrofuran) was initially screened, demonstrating the clear impact of using mixtures to improve the extraction yields (up to three-fold increase). After identifying ethyl acetate/ethanol/water as the solvent mixture with a greater capacity to extract carotenoids and lipids, the selective recovery of carotenoids and lipids was enhanced by optimizing the solvent mixture composition ratio. Envisioning the industrial application, an integrated biosolvent-based downstream platform was designed. Two different strategies were investigated to further isolate carotenoids and lipids from R. glutinis biomass and to recycle the ethyl acetate/ethanol/water mixture: (i) precipitation using cold acetone; (ii) sequential liquid–liquid extraction. The integrated process for each strategy was compared with a conventional extraction procedure in terms of recovery efficiencies and its environmental impact. Regardless of the strategy, it is shown that the mixture of ethyl acetate, ethanol and water (15/27/58% w/w) can be reused up to three consecutive extractive cycles, ensuring high extraction efficiency yields, while decreasing the process carbon footprint by about 75% compared to the conventional method.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...