Variability of sinapic acid derivatives during germination and their contribution to antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of broccoli sprouts on human plasma and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells†
Abstract
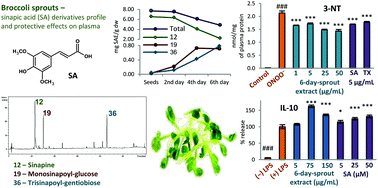
Broccoli sprouts represent a health-promoting food, rich in antioxidant and anti-inflammatory phytochemicals, among which sulfur compounds are most extensively investigated. In this study, the phenolics of broccoli sprouts (Brassica oleracea var. italica ‘Cezar’) were examined for variability during germination and influence on the bioactivity of sprouts. In the sprouts germinated in darkness, 31 compounds were identified by UHPLC-PDA-ESI-MS3 (18 sinapic acid derivatives, 8 glucosinolates, and 5 flavonoids) with sinapoyl components (SADs) prevailing among polyphenols. The total SADs decreased during germination (down to 4.85 mg per g dw in 6-day-sprouts), but the concurrent changes in molecular structures of the leading compounds (sinapine was replaced by sinapate sugar esters and sinapic acid) increased the antioxidant capacity of the sprouts. The glucosinolate-depleted 6-day-sprout extract (34.2 mg SADs per g dw) effectively protected human plasma components against peroxynitrite-induced oxidative damage in vitro (reduced the levels of 3-nitrotyrosine, lipid hydroperoxides and thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances) and enhanced the non-enzymatic antioxidant status of plasma. It also downregulated the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6) from LPS-stimulated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and increased the production of IL-10, an anti-inflammatory mediator. The relevant activity parameters of sinapic acid indicated that SADs might be linked to the observed effects. The results support the application of broccoli sprouts in oxidative stress- and inflammation-related diseases and the role of SADs as their bioactive components next to glucosinolates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...