Lysine inhibits apoptosis in satellite cells to govern skeletal muscle growth via the JAK2-STAT3 pathway†
Abstract
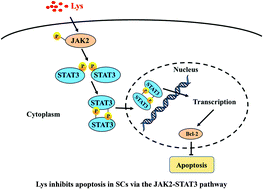
Apoptosis is programmed cell death that can be stimulated by external stress or nutrition restrictions. However, the precise mechanism of apoptosis in skeletal muscle remains unknown. The objective of this study was to investigate whether apoptosis could be regulated by lysine (Lys) supplementation and the potential mechanism. In this study, an isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantification (iTRAQ) proteomics analysis of the longissimus dorsi muscle from piglets showed that the Janus family tyrosine kinase (JAK)-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway was involved in Lys deficiency-induced apoptosis and inhibited skeletal muscle growth. Meanwhile, western blotting results demonstrated that Lys deficiency led to apoptosis in the longissimus dorsi muscle with the JAK2-STAT3 pathway inhibition. Interestingly, apoptosis was suppressed, and the JAK2-STAT3 pathway was reactivated after Lys re-supplementation. In addition, the results showed that Lys deficiency-induced apoptosis in satellite cells (SCs) was mediated by the JAK2-STAT3 pathway inhibition. Moreover, the JAK2-STAT3 pathway was reactivated by Lys re-supplementation and suppressed cell apoptosis, and this effect was inhibited after treatment with Tyrphostin B42 (AG 490). In conclusion, we found that Lys inhibits apoptosis in SCs to govern skeletal muscle growth via the JAK2-STAT3 pathway.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...