Mass cytometric study on the heterogeneity in cellular association and cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in primary human immune cells†
Abstract
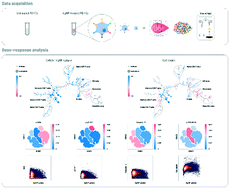
In recent years, there have been remarkable efforts to examine and understand the adverse effects of nanoparticles (NPs) on the environment and human health, not only qualitatively but also quantitatively. Mass cytometry has been developed for high-dimensional single-cell analyses and used to quantify the cellular association of inorganic NPs. Here, we have applied this novel technique to investigate the heterogeneity in cellular association and cytotoxicity of polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated silver nanoparticles with diameters of 10 nm and 20 nm in primary human immune cells. Our results revealed the cell-type-dependent heterogeneity in which AgNPs showed higher affinity to phagocytic cells like monocytes and dendritic cells than to other immune cell types. Upon exposure to AgNPs, these cells exhibited complex pro-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic responses, such as IκBα degradation, STAT1 phosphorylation and caspase-7 activation. Quantitative analyses of the single-cell dose–response relationship between the cellular AgNP association and signalling activities further revealed heterogeneity even within a monocyte population. The majority of cells belonged to the ‘low affinity’ subset, which showed a positive AgNP dose–cisplatin uptake (i.e. viability loss) correlation, as opposed to the remaining cells which belonged to the ‘high affinity’ subset and had an insignificant relationship between the cell-associated AgNP amount and cisplatin uptake/viability loss level. These subsets were distinctly responsive to the cellular AgNP content, as they showed different levels of signalling proteins such as IκBα, STAT1 and caspase-7. Our study can be helpful for further understanding the heterogeneous nature of cell–NP interactions and development of dose–response models at the single-cell level for various NPs, which will provide key information for the safe use of nanomaterials in biomedical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...