Direct C–H bond halogenation and pseudohalogenation of hydrocarbons mediated by high-valent 3d metal-oxo species
Abstract
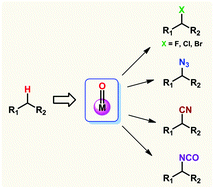
Late-stage direct functionalization of the C–H bond is synthetically desirable. Metalloenzymes having metal-oxo active sites are well known to selectively catalyze hydroxylation and halogenation reactions with high efficiency. This review highlights the recent developments in the field of direct C–H halogenation and pseudohalogenation reactions catalyzed by the functional models of metalloenzymes.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 Frontier and Perspective articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...