Al-doped Fe2O3 as a support for molybdenum oxide methanol oxidation catalysts†
Abstract
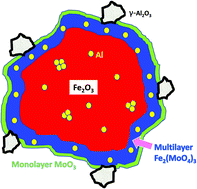
We have made high surface area catalysts for the selective oxidation of methanol to formaldehyde. This is done in two ways – (i) by doping haematite with Al ions, to increase the surface area of the material, but which itself is unselective and (ii) by surface coating with Mo which induces high selectivity. Temperature programmed desorption (TPD) of methanol shows little difference in surface chemistry of the doped haematite from the undoped material, with the main products being CO2 and CO, but shifted to somewhat higher desorption temperature. However, when Mo is dosed onto the haematite surface, the chemistry changes completely to show mainly the selective product, formaldehyde, with no CO2 production, and this is little changed up to 10% Al loading. But at 15 wt% Al, the chemistry changes to indicate the presence of a strongly acidic function at the surface, with additional dimethyl ether and CO/CO2 production characteristic of the presence of alumina. Structurally, X-ray diffraction (XRD) shows little change over the range 0–20% Al doping, except for some small lattice contraction, while the surface area increases from around 20 to 100 m2 g−1. Using X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) it is clear that, at 5% loading, the Al is incorporated into the Fe2O3 corundum lattice, which has the same structure as α-alumina. By 10% loading then it appears that the alumina starts to nano-crystallise within the haematite lattice into the γ form. At higher loadings, there is evidence of phase separation into separate Al-doped haematite and γ-alumina. If we add 1 monolayer equivalent of Mo to the surface there is already high selectivity to formaldehyde, but little change in structure, because that monolayer is isolated at the surface. However, when three monolayers equivalent of Mo is added, we then see aluminium molybdate type signatures in the XANES spectra at 5% Al loading and above. These appear to be in a sub-surface layer with Fe molybdate, which we interpret as due to Al substitution into ferric molybdate layers immediately beneath the topmost surface layer of molybdena. It seems like the separate γ-alumina phase is not covered by molybdena and is responsible for the appearance of the acid function products in the TPD.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Synchrotron Radiation Techniques in Catalytic Science


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...