Bilirubin analogues as model compounds for exciton coupling†
Abstract
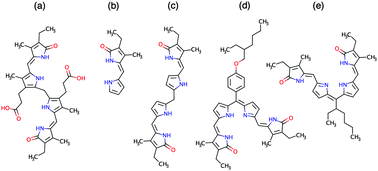
A series of phycobilin analogues have been investigated in terms of coupled excitonic systems. These compounds consist of a monomer, a tetrapyrrole structurally similar to bilirubin (bR), and two conjugated bR analogues. Spectroscopic and computational methods have been used to investigate the degree of interchromophore coupling. We find the synthesised bR analogue shows stronger excitonic coupling than bR, owing to a different molecular geometry. The excitonic coupling in the conjugated molecules can be controlled by modifying the bridge side-group. New computed energy levels for bR using the DFT/MRCI method are also presented, which improve on published values and re-assign the character of excited singlet states.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...