The pH dependent mechanisms of non-enzymatic peptide bond cleavage reactions†
Abstract
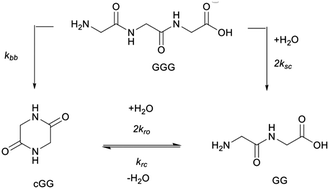
The non-enzymatic cleavage rates of amide bonds located in peptides in aqueous solution is pH-dependent and involves two distinct mechanisms: direct hydrolysis (herein termed “scission”) and intramolecular aminolysis by the N-terminal amine (herein termed “backbiting”). While amide bond cleavage has been previously characterized using a variety of peptides, no systematic study has yet been reported addressing the effect of the pH on the interplay between the two amide bond cleavage pathways. In this study, the cleavage rates of the glycine dimer (GG), the glycine trimer (GGG), and the cyclic dimer (cGG), as well as the alanine trimer (AAA), were measured at pH 3, 5, 7, and 10 at 95 °C employing quantification based on 1H NMR. The distinct rate constants for scission and backbiting processes were obtained by solving the differential rate equations associated with the proposed kinetic model. Generalizations concerning the relative importance of the various amide bond cleavage pathways at pH 3, 5, 7, and 10 are presented. In particular, scission dominates at pH 10, while backbiting dominates at neutral pH. At the acidic pH of 3, both backbiting and scission are significant. The model of the reaction network, used in this work, enables the quantification of these multiple competing mechanisms and can be applied to longer peptides and to similar types of reaction networks.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...