Light-triggered syneresis of a water insoluble peptide-hydrogel effectively removes small molecule waste contaminants†
Abstract
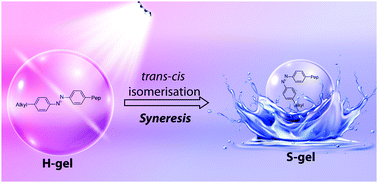
A short peptide based hydrogel exhibits aqueous insolubility, thixotropy and efficient light induced syneresis. Upon irradiation with UV light, the hydrogel shrinks and expells ∼50% of the solvent. Syneresis is caused by light-triggered trans–cis isomerisation of an azobenzene moiety in the peptide derivative. This expulsion of solvent can be effectively exploited in the removal of low molecular weight contaminants in water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...