Biopolymers-calcium phosphate antibacterial coating reduces the pathogenicity of internalized bacteria by mesenchymal stromal cells†
Abstract
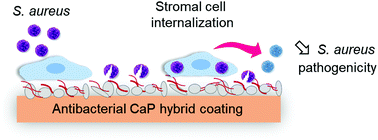
A multifunctional material system that kills bacteria and drives bone healing is urgently sought to improve bone prosthesis. Herein, the osteoinductive coating made of calcium phosphate/chitosan/hyaluronic acid, named Hybrid, was proposed as an antibacterial substrate for stromal cell adhesion. This Hybrid coating possesses a contact-killing effect reducing by 90% the viability of Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Gram-negative Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) strains after 48 h of contact. In addition to the production of immunomodulatory mediators, Wharton's jelly (WJ-SCs), dental pulp (DPSCs) and bone marrow (BM-MSCs) derived stromal cells were able to release antibacterial and antibiofilm agents effective against S. aureus and P. aeruginosa strains, respectively. Studying the effect of the Hybrid coating on the internalization of S. aureus by the stromal cells, in acute-mimicking bone infection, highlighted an increase in the bacteria internalization by DPSCs and BM-MSCs when cultured on the Hybrid coating versus uncoated glass. Despite the internalization, Hybrid coating showed a beneficial effect by reducing the pathogenicity of the internalized bacteria. The formation of biofilm was reduced by at least 50% in comparison to internalized bacteria by stromal cells on uncoated glass. This work opens the route for the development of innovative antibacterial coatings by taking into account the internalization of bacteria by stromal cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...