Topography induced stiffness alteration of stem cells influences osteogenic differentiation†
Abstract
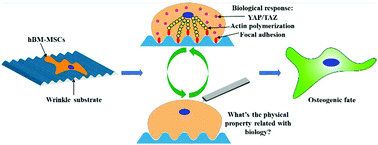
Topography-driven alterations in cell morphology tremendously influence cell biological processes, particularly stem cell differentiation. Aligned topography is known to alter the cell shape, which we anticipated to also induce altered physical properties of the cell. Here, we show that topography has a significant influence on single cell stiffness of human bone marrow derived-Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hBM-MSCs) and the osteogenic differentiation of these. Aligned topographies were used to control the cell elongation, depicted as the cell aspect ratio (CAR). Intriguingly, an equal CAR elicited from different topographies, resulted in highly altered differentiation behavior and the underlying single cell mechanics was found to be critical. The cell behavior was found to be focal adhesion-mediated and induced stiffness alterations rather than just influencing the cell elongation. The effect was further corroborated by investigations of the transcriptional regulators YAP. Our study provides insight into how mechanical properties of the cell, which are stimulated by topography, modulate the osteogenesis of hBM-MSCs, which is beneficial for improving the understanding of interactions between stem cells and topography for developing applications of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...