Keto-salicylaldehyde azine: asymmetric substituent effect on their optical properties via electron-donating group insertion†
Abstract
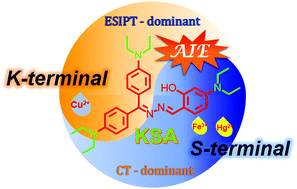
Organic fluorescent probes have attracted increasing attention owing to their high sensitivity and recognition ability, structurally adjustable flexibility and manifestation in the form of visualization. Salicylaldehyde azine (SAA) and its derivatives exhibit a great potential for practical applications, but the synthesis of SAA asymmetric compounds in low yields, serving multiple functions, is cumbersome. As an alternative building block, Keto-Salicylaldehyde Azine (KSA) was developed by our group for constructing various AIEgens via an excited state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) process to detect some cellular organelles and specific metal ions. For illuminating the structure–property relationship of the two asymmetric sides in a KSA unit, DPAS was employed as a model and the N,N-diethyl group with electron-donating effects was introduced on its salicylaldehyde side (S-terminal) and diphenylketone side (K-terminal). Three new derivatives were obtained and showed different photophysical properties, particularly in AIE performance and metal ion responsiveness, implying that their intrinsic electronic structure can be easily affected by the asymmetric substitution effect. Therefore, this study is a meaningful and valuable reference for KSA modification on expanding fluorescent probes with various functions via the purposeful regulation of their chemical structure, by either modifying the K-terminal or the S-terminal.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...