Improving LMOF luminescence quantum yield through guest-mediated rigidification†
Abstract
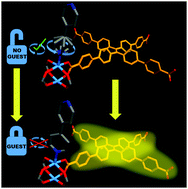
Luminescent metal–organic frameworks (LMOFs) are among the fastest growing solid-state optical materials and have been studied for a wide variety of applications. However, when developing a new LMOF, it can be challenging to balance a strong luminescence quantum yield with all other important properties required by the intended application (appropriate excitation/emission wavelengths, chemical and physical stability, low toxicity, etc.). Being able to post-synthetically improve a LMOF's quantum yield is valuable, as it offers additional tunability in materials design and modification. As framework flexibility can limit quantum yield, post-synthetic methods of rigidifying an LMOF have the potential to improve its performance. This paper discusses a pair of nearly identical isoreticular LMOFs, and uses them as a model system to investigate how framework flexibility affects quantum yield. Introducing optically-inactive guests into a LMOF pore is shown to be an effective method for rigidifying the framework, improving the quantum yield of a flexible LMOF from 12.2% to 59.3%—an improvement of nearly 400%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...