Dynamic magnetic properties and spin pumping in polymer-assisted-deposited La0.92MnO3 thin films
Abstract
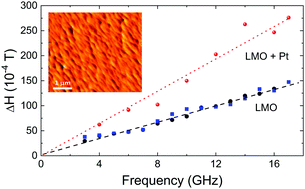
Complex oxide thin films grown by using chemical methods are of strong interest because of their low-cost, environment friendly fabrication and easy scalability. However, their introduction in spintronic applications or magnetic devices is still scarce mainly because of concerns regarding their interfacial quality. Here, we report on the preparation by polymer-assisted-deposition (PAD) of epitaxial La0.92MnO3 (LMO) thin films. We demonstrate that ferromagnetic conducting LMO thin films with smooth surfaces (rms ∼ 0.2 nm) can be prepared by PAD. By means of temperature-dependent broadband ferromagnetic resonance (FMR), we show that the LMO film exhibits a four-fold in-plane anisotropy, with [110] being the easy in-plane axis, compatible with strain release from the rhombohedral bulk phase. It has also been found that the isotropic Gilbert damping, α, determined from the broadening of the FMR linewidth, does not show a relevant extrinsic contribution and it exhibits an intraband-like temperature dependence, i.e. it increases as temperature decreases. By capping LMO thin films with a 10 nm thick Pt layer deposited ex situ, damping is substantially enhanced, from a value at 150 K of αLMO ∼ 1 × 10−2 for the bare LMO film to αLMO+Pt ∼ 2.5 × 10−2 for the Pt capped film. This strong increase of magnetic damping is indicative of the transfer of spin momentum from LMO to the Pt layer by spin pumping. Our results demostrate that LMO films grown by PAD may be used as efficient spin source systems in heterostructures for spintronic devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...