Stretchable liquid metal electromagnetic interference shielding coating materials with superior effectiveness†
Abstract
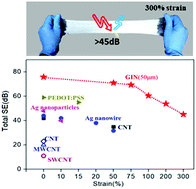
Flexible electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials typically exhibit poor stretchability due to the break of electronic transport, which makes shielding efficiency decrease sharply with discontinuous conductivity. This electric-mechanical contradiction is limiting for soft electronics and other emerging applications that require materials with both high shielding performance and low mechanical stiffness. Here, this constraint is overcome with a liquid metal amalgam that exhibits superior metal conductivity and the capability to undergo large deformation (up to 300% strain). This amalgam is mainly composed of GaIn24.5, Ni particles and gallium oxide. A substrate decorated with this amalgam demonstrated excellent EMI shielding effectiveness of over 75 dB at frequencies of 100 kHz–18 GHz owing to its excellent conductivity; furthermore, this material can satisfy military shielding requirements (>60 dB) even at strains of up to 75%. Besides, this amalgam, as a non-Newtonian fluid, can facilely decorate various substrates with irregular shapes because it has good adhesion and superb flexibility. The exceptional combination of shielding performance and mechanical properties is enabled by large-scale deformability of the liquid metal to create a continuous conductive path, even under extreme stretching conditions. This material provides a brand new perspective for stretchable shielding applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...