Structural coloration by inkjet-printing of optical microcavities and metasurfaces†
Abstract
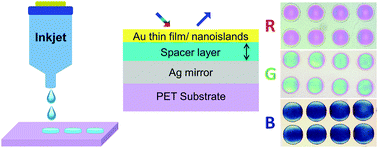
Structural color generation by plasmonic and other means has attracted significant interest as a solution to avoid inks based on dyes. Prominent advantages include better robustness compared with organic dyes while also providing high chromaticity and brightness in ultrathin films. However, lack of cheap and scalable fabrication techniques has so far limited structural coloration to only a few applications and functional devices. Here, we demonstrate reflective (plasmonic) structural coloration at high resolution by inkjet printing on non-patterned surfaces. The method is flexible, scalable to large areas, and avoids complicated or costly fabrication steps. Optical microcavities on flexible plastic substrates were made starting with an inkjet-printed silver film as a bottom mirror. Inkjet-printed organic dielectric micropixels then served as the spacer layer, resulting in optical microcavities with reflective structural colors after coating with a thin semi-transparent metallic top layer. Optimization of ink formulation allowed for uniform pixels with minimum coffee stain effects as well as control of spacer thickness (around 50–150 nm) and color by varying the solid content of the ink. We investigate the possibility to obtain red, green and blue (RGB) pixels and demonstrate the improvement of particularly the blue coloration using wavelength-dependent plasmon absorption of gold nanoislands as a top mirror. Inkjet printing of optical microcavities and plasmonic cavities may find use in various applications, such as reflective displays in color.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...