Smart, chiral, and nonconjugated cyclohexane-based bis-salicylaldehyde hydrazides: multi-stimuli-responsive, turn-on, ratiometric, and thermochromic fluorescence, single-crystal structures via DFT calculations†
Abstract
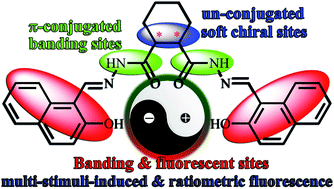
A unique series of smart, chiral, and multi-stimuli-responsive cyclohexane-based bis-salicylaldehyde hydrazides have been designed and prepared. Their molecular structures, alignments, and fluorescence properties are highly dependent on the environmental conditions. They show unusual polar-solvent-, cation-, anion-, and amino-acid-induced fluorescence enhancements with emission quantum yield of up to 0.40. Based on single-crystal structures and multi-molecule density functional theory calculations, it was shown that polar-solvent-induced fluorescence can be caused by the intermolecular hydrogen bonds that would affect the molecular structure, charge distribution, and transition process. Cation- and anion/amino-acid-induced fluorescence are caused by coordination and deprotonation, respectively. Through cation/anion exchange reactions, ratiometric fluorescence along with extending the detection range for Mg2+ has been achieved for the first time. Thermochromic fluorescence from white into blue would be observed when the temperature is increased from 77 K to room temperature. Moreover, these nonconjugated materials with lower cytotoxicity and better biocompatibility have potential applications in cell imaging and chiral recognition.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...