Multichannel photoluminescence tuning in Eu-doped apatite phosphors via coexisting cation substitution, energy transfer and valence mixing†
Abstract
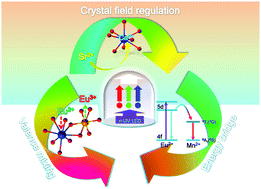
Various strategies including cation substitution, energy transfer in a variety of cation sites and valence mixing of Eu2+/Eu3+ in a single compound have offered significant advantages in tuning the photoluminescence properties of phosphors for white light-emitting diodes (W-LEDs). Herein, we report a series of Eu2+-doped Ca9−xSrxLiGd2/3(PO4)7 solid solution phosphors of the apatite type prepared by a traditional high-temperature solid-state reaction. The crystal field regulation around the Eu2+ ions causes different luminescence behaviors of the two-peak emission and induces photoluminescence tuning as a function of strontium content. In addition to the emission band peak at 423 nm in Ca9LiGd2/3(PO4)2:0.03Eu2+, another broad-band peak at 485–535 nm is observed with Sr2+ substitution, which is attributed to the combined effect of the crystal field splitting and energy transfer between Eu2+ ions. In pursuit of precise color luminescence tuning, we designed the Eu2+ → Mn2+ energy transfer and studied the cooperative performance of mixed-valent Eu2+/Eu3+ in the solid solution phosphors with different compositions (x = 0, 4.5, 9.0), and the corresponding luminescence mechanisms were proposed and discussed in detail. Finally, a representative W-LED device composed of a 370 nm UV chip and Sr8.75LiGd2/3(PO4)7:0.05Eu2+,0.20Mn2+ sample could present excellent electroluminescence performance with the parameters Ra = 90.4, CCT = 3794 K and color coordinate (0.385, 0.388), which could well meet the commercial standard of warm white light. Therefore, the results suggest that these three luminescence tuning strategies are feasible to be simultaneously applied in other phosphor systems for precise emission tuning and obtaining efficient white emitting phosphors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...