All-printed, low-cost, tunable sensing range strain sensors based on Ag nanodendrite conductive inks for wearable electronics†
Abstract
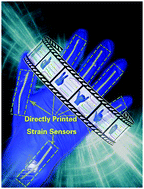
Flexible and wearable strain sensors with high stretchability and high sensitivity have been studied intensively. However, the achievement of low-cost, rapid mass production and high performance of wearable strain sensors remains a challenge. In this study, Ag nanodendrite (ND) inks with good printability for varieties of substrates are prepared, which can be directly screen-printed onto nitrile rubber to manufacture strain sensors. Printed strain sensors (PSSs) with diverse working strain ranges and sensitivities can be simultaneously obtained by printing versatile geometric patterns. Comparatively, straight-line PSSs with a linewidth of 2 mm exhibit high electrical conductivity (1.14 × 105 S m−1), a large sensing range (105%), high sensitivity (maximum gauge factor = 294.3), an ultrafast response time (18 ms), and long-term stability (more than three weeks). Additionally, the sensing mechanism of the PSSs is further investigated by observing their surface topographies. Eventually, a smart glove based on PSSs is used for monitoring human motion (finger bending, wrist bending, walking, etc.) and gesture actions, demonstrating the potential applications of Ag ND-based PSSs in wearable electronic devices and human–machine interaction intelligent systems.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 Journal of Materials Chemistry C Most Popular Articles

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...