Mitochondria-targeted tetrahedral DNA nanostructures for doxorubicin delivery and enhancement of apoptosis†
Abstract
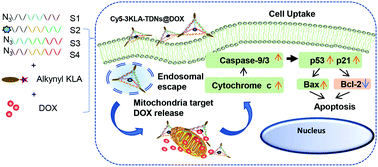
Mitochondria-targeted nanoparticles, such as liposomes, polymers and inorganic particles, suffer from heterogeneity, low biocompatibility and low drug loading efficiency. Here, we present a novel delivery platform based on tetrahedral DNA nanostructures (TDNs) that enable the mitochondrial transportation of the anticancer drug doxorubicin (DOX) for cancer therapy. In our design, DOX was intercalated into TDNs, which executed the cell-killing function inside the tumor cells. Various numbers of D-(KLAKLAK)2 (KLA) were conjugated to TDNs to achieve the mitochondria targeting effect. The mean size of the KLA-modified TDNs was about 15 nm, and the TDNs were stable in FBS. The DOX loading efficiency of the TDNs was up to around 77%. The 3KLA-modified TDNs exhibited the most efficient DOX accumulation in mitochondria, leading to an effective release of cytochrome c, and the upregulated expression levels of caspase-9, caspase-3, p21 and p53. Meanwhile, 3KLA-TDNs/DOX elevated the pro-apoptotic Bax, reduced the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein expression and increased the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, which finally activated the mitochondria-mediated, programmed apoptosis pathway to enhance the anticancer efficacy in vitro. This 3KLA-TDN and DOX co-assembling strategy can be further developed to transport other anthracyclines and chemotherapeutic agents for enhanced apoptosis effects.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...