A chitosan modified asymmetric small-diameter vascular graft with anti-thrombotic and anti-bacterial functions for vascular tissue engineering†
Abstract
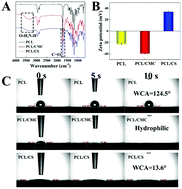
Rapid endothelialization and prevention of restenosis are two vital challenges for the preparation of a small-diameter vascular graft (SDVG), while postoperative infection after implantation is often neglected. In the present study, carboxymethyl chitosan (CMC) and chitosan (CS) were chosen as the anti-thrombotic and anti-bacterial components, respectively; and then an asymmetric vascular graft was fabricated by co-electrospinning of poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL)/CMC and PCL/CS. The mechanical properties of the asymmetric vascular graft were much better than those of the native vessels. In vitro blood compatibility tests indicated that the inner layer of the graft could inhibit thrombosis effectively. The outer layer of the graft had a certain anti-bacterial effect owing to the addition of chitosan. Besides, the inner layer of the graft could greatly promote the growth of endothelial cells. It is believed that the asymmetric SDVG with anti-thrombotic and anti-bacterial functions could contribute to the future clinical implantation of tissue engineered vascular grafts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...