Fenton-reaction-stimulative nanoparticles decorated with a reactive-oxygen-species (ROS)-responsive molecular switch for ROS amplification and triple negative breast cancer therapy
Abstract
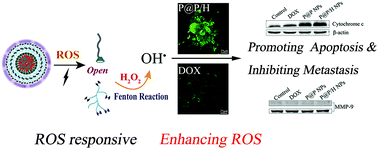
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is characterized by a high metastatic rate, which can seriously threaten women's health. ROS play an important role in tumor development and metastasis. Excessive ROS can induce tumor cell apoptosis and inhibit tumor cell metastasis. This study investigated Fenton-reaction-stimulative nanoparticles (P@P/H NPs) containing ROS-responsive molecular switches for antitumor metastasis by amplifying the ROS and activating the cascade biological reaction of ROS in tumor cells. Spheroidal P@P/H NPs exhibited a uniform size of 68.18 ± 0.29 nm, high drug cumulative release of 97.59% in response to H2O2 at 24 h, and satisfactory cytotoxicity with the IC50 value of 0.50 ± 0.02 μg mL−1. The markedly elevated ROS level caused by P@P/H NPs generated an evident antitumor metastasis effect in vitro by facilitating the expressions of cytochrome c, caspase-9, and caspase-3 and blocking that of matrix metalloprotein 9 (MMP-9). Moreover, P@P/H NPs engendered an excellent tumor inhibition rate of 56.37% and antitumor metastasis effect in vivo. Therefore, P@P/H NPs could respond to H2O2 in tumor cells to rapidly disassemble and further increase the ROS to induce antitumor metastasis via the Fenton reaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...