Redox-responsive tetraphenylethylene-buried crosslinked vesicles for enhanced drug loading and efficient drug delivery monitoring†
Abstract
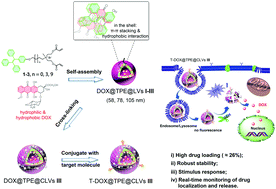
Liposomes have been applied extensively as nanocarriers in the clinic (e.g., to deliver anticancer drugs) due to their biocompatibility and internal cavity structures. However, their low drug-loading capacity (DLC; <10%) and uncontrolled release reduce their efficacy in cancer treatment. To improve the DLC and monitor release of drugs in cells in real-time, stimuli-responsive vesicles must be developed. We present various amphiphilic tetraphenylethylene (TPE)-containing compounds designed to self-assemble into liposome-like vesicles that can load both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. The highest DLC for doxorubicin (DOX) was ≤26% for vesicles (diameter = 105 nm) that could encapsulate hydrophilic DOX in the interior water pool and hydrophobic DOX via π–π stacking interactions between DOX and the TPE moiety. The stable vesicles could respond rapidly to overexpressed glutathione in the tumor microenvironment to release loaded DOX for cancer therapy. Vesicles modified by active targeting groups showed more efficacious tumor treatment compared with unmodified vesicles and free DOX in vitro and in vivo. Simultaneously we observed, spatiotemporally, the subcellular location of the delivery system and release process of DOX. Our work provides a novel nano-engineering technology to integrate the desired properties for anticancer theranostics: high DLC, stability, stimuli-responsiveness to the cancer environment, drug-delivery monitoring, active targeting, and suppression of tumor growth. These novel vesicles could be employed as multifunctional drug-delivery systems for cancer therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...