Polyphenol-based nanoplatform for MRI/PET dual-modality imaging guided effective combination chemotherapy†
Abstract
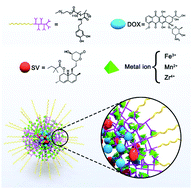
Combination therapy with multiple chemotherapeutic agents is the main approach for cancer treatment in the clinic. Polyphenol-based materials are found in our diet, demonstrate good biocompatibility, and prevent numerous diseases. In this study, we encapsulate two drugs in a single polyphenol-based polymer with Fe3+ or Mn2+ ions as the cross-linker for cancer therapy. The combination index of two drugs is an essential parameter to evaluate drug combinations. The amphiphilic polymer poly(ethylene glycol)-block-polydopamine (PEG–PDA) was prepared by RAFT polymerization. The nanoparticles were prepared via self-assembly with Fe3+ or Mn2+ ions. Both doxorubicin (DOX) and simvastatin (SV) were encapsulated in the core of the nanoparticles. The cell viability and combination index were evaluated in vitro. The tumor accumulation of the nanoparticles was investigated by positron-emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. The as-prepared nanoparticles exhibited high drug loading capacity. The drug loaded nanoparticles could kill cancer cells effectively with a combination index <1. Both PET and MRI revealed that the nanoparticles showed long blood circulation time and high tumor accumulation. The nanoparticles could inhibit tumor inhibition via intravenous injection of nanoparticles. The polyphenol-based nanoplatform may serve as a promising theranostic candidate for clinical application.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...