Cytosolic delivery of quantum dots mediated by freezing and hydrophobic polyampholytes in RAW 264.7 cells†
Abstract
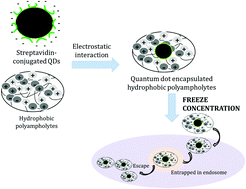
Quantum dots (QDs) can be delivered efficiently inside macrophages using a freeze-concentration approach. In this study, we introduced a new, facile, high concentration-based freezing technology of low toxicity. We also developed QD-conjugated new hydrophobic polyampholytes using poly-L-lysine (PLL), a naturally derived polymer, which showed sustained biocompatibility, stability over one week, and enhanced intracellular delivery. When freeze-concentration was applied, the QD-encapsulated hydrophobic polyampholytes showed a higher tendency to adsorb onto the cell membrane than the non-frozen molecules. Interestingly, we observed that the efficacy of adsorption of QDs on RAW 264.7 macrophages was higher than that on fibroblasts. Furthermore, the intracellular delivery of QDs using hydrophobic polyampholytes was higher than those of PLL and QDs. In vitro studies revealed the efficient endosomal escape of QDs in the presence of hydrophobic polyampholytes and freeze-concentration. Collectively, these observations indicated that the promising combination of freeze-concentration and hydrophobic polyampholytes may act as an effective and versatile strategy for the intracellular delivery of QDs, which can be used for biological diagnosis and therapeutic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...