Understanding how charge and hydrophobicity influence globular protein adsorption to alkanethiol and material surfaces†
Abstract
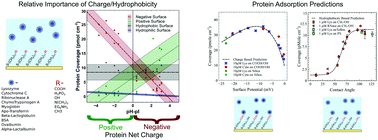
Every biosensor, bioengineered scaffold or biomedical implant depends crucially on an ability to control protein adsorption at the material surface. Yet the adsorption of proteins to solid surfaces in aqueous media is a complex and poorly understood phenomenon. To gain further insights we study protein adsorption using the quartz crystal microbalance for 10 model globular proteins interacting with positive, negative, neutral, hydrophobic and mixed alkanethiol monolayers as well as silica, polystyrene and Teflon, equating to approximately 200 protein–surface combinations. The charge state of the materials in liquid was measured with atomic force microscopy using a colloidal probe and numerically solving the full non-linear Poisson–Boltzmann equation. This approach has allowed us to address some of the important questions surrounding the basic principles that govern protein adsorption including the relative importance of net charge and hydrophobicity and why some materials are protein resistant. With our set of mixed monolayer surfaces, we can modulate charge over a wide range whilst eliminating hydrophobic interactions and vice versa – thus permitting determination of the functional dependence of adsorption on these parameters. This has led us to develop two empirical predictive models with up to 90% accuracy that together encompass most materials relevant to biotechnological and biomedical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...